NEBULA



NEBULA
A nebula (from Latin: "cloud"; pl. nebulae with ligature or nebulas) is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Originally, nebula was a name for any diffuse astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy, for instance, was referred to as the Andromeda Nebula(and spiral galaxies in general as "spiral nebulae") before the true nature of galaxies was confirmed in the early 20th century by Vesto Slipher, Edwin Hubble, etal. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Eagle Nebula. This nebula is depicted in one of NASA's most famous images, the "Pillars of Creation". In these regions the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form larger masses, which attract further matter, and eventually will become massive enough to form stars. The remaining materials are then believed to form planets, and other planetary system objects.
Many nebulae or stars form from the gravitational collapse of gas in the interstellar medium or ISM. As the material collapses under its own weight, massive stars may form in the center, and their ultraviolet radiation ionizes the surrounding gas, making it visible at optical wavelengths. Examples of these types of nebulae are the Rosette Nebula and the Pelican Nebula. The size of these nebulae, known as HII regions, varies depending on the size of the original cloud of gas. New stars are formed in the nebulas. The formed stars are sometimes known as a young, loose cluster.
Some nebulae are formed as the result of supernova explosions, the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The materials thrown off from the supernova explosion are ionized by the energy and the compact object that it can produce. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. The supernova event was recorded in the year 1054 and is labelled SN 1054. The compact object that was created after the explosion lies in the center of the Crab Nebula and is a neutron star.
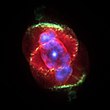
Other nebulae may form as planetary nebulae. This is the final stage of a low-mass star's life, like Earth's Sun. Stars with a mass up to 8–10 solar masses evolve into red giants and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their atmospheres. When a star has lost enough material, its temperature increases and the ultraviolet radiation it emits can ionize the surrounding nebula that it has thrown off. The nebula is almost 97% hydrogen and 3% helium, plus trace amounts of other elements.
Types of nebulae
Classical types
Objects named nebulae belong to four major groups. Before their nature was understood, galaxies ("spiral nebulae") and star clusterstoo distant to be resolved as stars were also classified as nebulae, but no longer are.
- H II regions, large diffuse nebulae containing ionized hydrogen
- Planetary nebulae
- Supernova remnant (e.g., Crab Nebula)
- Dark nebula
Not all cloud-like structures are named nebulae; Herbig–Haro objects are an example.